Introduction
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses approach their IT infrastructure. With the wide range of benefits offered by the cloud, more and more organizations are migrating their applications and data to cloud environments. However, with so many different deployment models to choose from, it can be challenging to determine which is the best fit for your specific needs. In this blog, we’ll take a deep dive into the four main cloud deployment models: Public Cloud, Private Cloud, Hybrid Cloud, and Multi-Cloud.
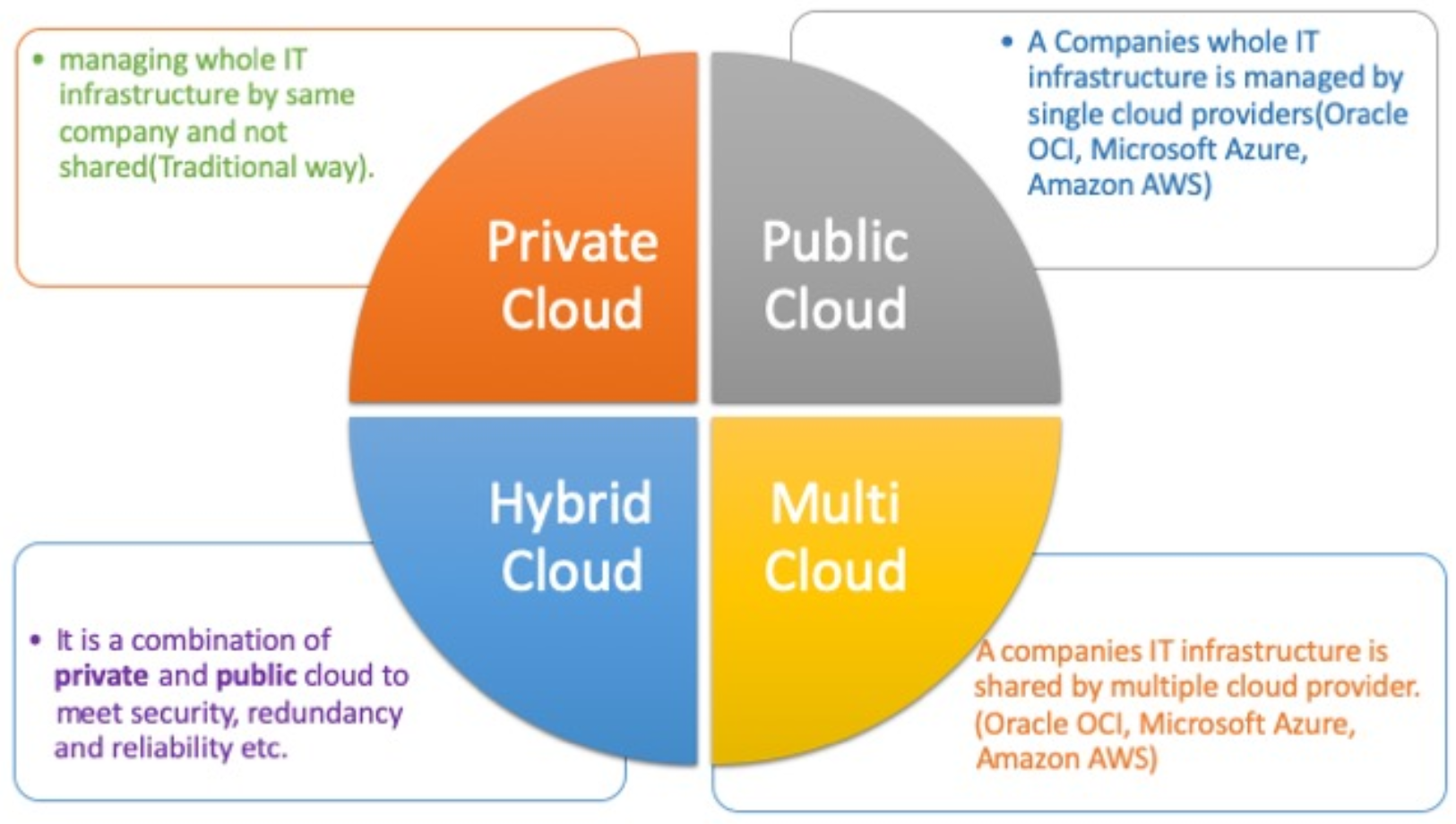
We’ll explore the unique characteristics of each model, provide real-life examples of their applications, and share best practices for implementation. Whether you’re new to cloud computing or looking to optimize your existing cloud infrastructure, this blog is your guide to understanding the fascinating world of cloud deployment models. So, let’s begin our journey!
Public Cloud
Public Cloud refers to a cloud deployment model where infrastructure and services are provided by third-party providers over the Internet. This means that instead of investing in hardware and infrastructure, companies can use the resources of public cloud providers like AWS, Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud Platform. The public cloud is characterized by shared resources and ease of access, making it a popular choice for many organizations.
Benefits of Public Cloud:
- Cost-effective: One of the primary benefits of using public cloud services is that you only pay for the resources you consume. This means that you don’t have to invest in expensive hardware or infrastructure upfront, which can be significant cost savings for many organizations.
- Scalable: Public cloud services are designed to be highly scalable, which means that you can easily scale resources up or down as needed. This makes it easy for organizations to handle fluctuations in demand without having to worry about infrastructure or hardware limitations.
- Accessible: Public cloud services can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection, which makes it easy for employees to work remotely or access resources while on the go.
Real-life example:
1. Spotify: It is a popular music streaming service that uses Google Cloud for its infrastructure. By leveraging the power of Google Cloud, Spotify can scale its services to millions of users globally while minimizing costs. This is a great example of how public cloud services can be used to support a global, high-traffic service.
2. Netflix: The popular video streaming service, Netflix, also relies on AWS for its infrastructure needs. This allows Netflix to easily scale its services to millions of users globally.
Best practices for Public Cloud:
- When using public cloud services, it’s important to implement robust security measures to protect your data and applications. This includes using encryption, access controls, and other security measures to ensure that your data is safe from unauthorized access.
- Additionally, it’s important to regularly monitor usage to optimize costs and performance. This means keeping an eye on resource usage and adjusting your usage patterns to minimize costs and improve performance.
Private Cloud
Private Cloud is a cloud deployment model where organizations own and manage the infrastructure, often on-premises or in a data center. Unlike Public Cloud, Private Cloud provides a dedicated, isolated environment for an organization’s computing resources and services. Private Cloud is suitable for organizations that require a high degree of control and customization over their infrastructure and applications.
Benefits of Private Cloud:
- Customization: Private Cloud provides complete control over the infrastructure and services, allowing organizations to tailor them to their specific needs. This customization results in higher performance, better availability, and faster time-to-market for applications.
- Security: Private Cloud offers higher levels of security than the Public Cloud because organizations have complete control over the infrastructure and can implement strict security measures. Private Clouds are suitable for organizations that require strict compliance with data protection regulations like HIPAA, PCI DSS, and GDPR.
- Cost-effectiveness: Private Cloud can be cost-effective compared to Public Cloud for organizations with stable and predictable workloads. The private cloud eliminates the need for upfront capital expenditures on hardware and infrastructure, and organizations only pay for the resources they use.
Real-life example:
NASA: NASA uses a Private Cloud to process large amounts of scientific data from space missions. NASA needs complete control over the infrastructure to comply with strict security regulations and to handle the massive data volumes generated by space missions.
Banks: Financial institutions such as banks, use Private Clouds to store and process sensitive financial information.
Government agencies: They often use Private Clouds to ensure data sovereignty and comply with strict security and privacy regulations.
Best practices for Private Cloud:
- Plan the infrastructure carefully, considering factors like capacity, performance, and security. Organizations should start with a clear understanding of their business requirements and use cases before designing and implementing the Private Cloud infrastructure.
- Invest in security measures like intrusion detection systems, firewalls, and regular vulnerability assessments. Organizations should also implement access controls, data encryption, and disaster recovery solutions to protect their data and applications.
- Train your IT team to manage the system effectively and stay up-to-date with industry best practices. Organizations should also consider partnering with experienced cloud service providers or consultants to help with the planning, implementation, and ongoing management of their Private Cloud.
- Regularly monitor and optimize usage to achieve cost-effectiveness. Organizations should continuously monitor the Private Cloud infrastructure to identify opportunities for optimization, such as right-sizing instances, consolidating workloads, and automating resource provisioning and scaling.
Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid Cloud is a cloud deployment model that combines Public and Private Clouds, allowing businesses to leverage the benefits of both environments. This approach enables organizations to keep sensitive data and applications in a secure Private Cloud while using Public Cloud resources for less critical workloads.
Benefits of Hybrid Cloud:
- Flexibility: You can choose the best cloud deployment model for each workload, depending on factors like cost, performance, and security.
- Cost savings: By using Public Cloud resources for less critical workloads, you can reduce overall infrastructure costs.
- Improved security: Sensitive data and applications can be kept in a secure Private Cloud, while less critical workloads run on Public Clouds.
Real-life examples:
Adobe Systems: Adobe Systems, a software company, uses a Hybrid Cloud approach to deliver its Creative Cloud services. Adobe’s Private Cloud infrastructure handles sensitive data like customer account information, while Adobe leverages Public Cloud resources for less critical workloads like rendering video projects.
The New York Times: The New York Times, a media organization, uses a Hybrid Cloud approach to support its online presence. The company stores its archives and sensitive data in a Private Cloud while using Public Cloud resources for online content delivery during peak traffic times.
Best practices for Hybrid Cloud:
- Establish clear communication between public and private resources to ensure seamless integration and data exchange.
- Use a unified management platform to monitor and manage resources across both cloud environments.
- Plan for disaster recovery scenarios and implement appropriate data backup and restoration processes.
- Ensure consistent security measures across both cloud environments, including identity and access management, encryption, and regular vulnerability assessments.
Multi-Cloud
Multi-Cloud deployment is becoming increasingly popular as organizations look to take advantage of the unique strengths of different cloud providers. Here’s some additional information and real-life examples:
Benefits of Multi-Cloud:
- Improved performance: By leveraging different providers’ strengths, organizations can optimize performance for each workload.
- Better compliance: Multi-Cloud deployments allow organizations to store data in different regions or jurisdictions to comply with specific data sovereignty laws.
- Future-proofing: By avoiding vendor lock-in, organizations can adapt to changing market trends or switch providers if necessary.
Real-life example:
The Weather Company: The Weather Company, a subsidiary of IBM, uses a Multi-Cloud deployment to provide real-time weather data to businesses and governments. They use AWS for their global content delivery network, Google Cloud for their data analytics, and IBM Cloud for their on-premises data centers. This approach allows them to provide accurate, up-to-date weather information to customers worldwide.
Best practices for Multi-Cloud:
- Choose cloud providers that offer interoperability to ensure seamless integration between different cloud environments.
- Use automation to streamline multi-cloud management tasks and reduce the risk of human error.
- Develop a governance framework that covers all cloud providers to ensure consistent security, compliance, and performance.
Conclusion
The cloud deployment model you choose for your organization has a significant impact on your operations and overall success. It’s important to carefully evaluate the benefits and drawbacks of each model, as well as consider your organization’s specific needs and goals.
Public Cloud offers cost savings, scalability, and accessibility but may not provide the level of security and control needed for sensitive data. Private Cloud provides customization, security, and performance but may require significant upfront investment and ongoing maintenance. Hybrid Cloud offers flexibility, cost savings, and improved security by combining public and private cloud resources. Multi-Cloud offers flexibility, reduced risk, and cost optimization by utilizing multiple cloud providers.
Real-life examples from various industries demonstrate the effectiveness of each cloud deployment model in meeting specific business needs. Implementing best practices for each model, such as planning infrastructure carefully, investing in security measures, using management tools, and developing clear strategies, can help organizations optimize their cloud infrastructure and minimize risks.
Moreover, incorporating storytelling and real-life examples into your content can engage your audience and help them better understand the practical application of cloud computing in various industries. With the right cloud deployment model and a solid understanding of its benefits and challenges, businesses can leverage the power of cloud computing to drive innovation and growth.
To read the previous article, visit:
https://pravinmishra.in/building-a-better-cloud-impact-of-aws-on-technology
To check our offered courses, visit:
